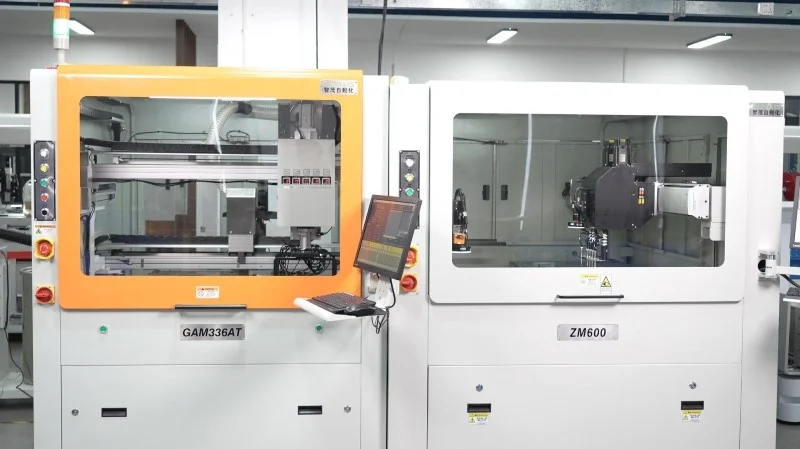
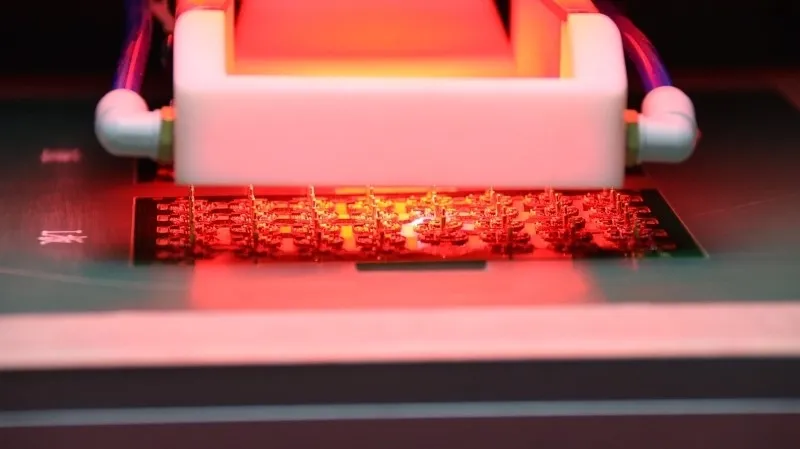
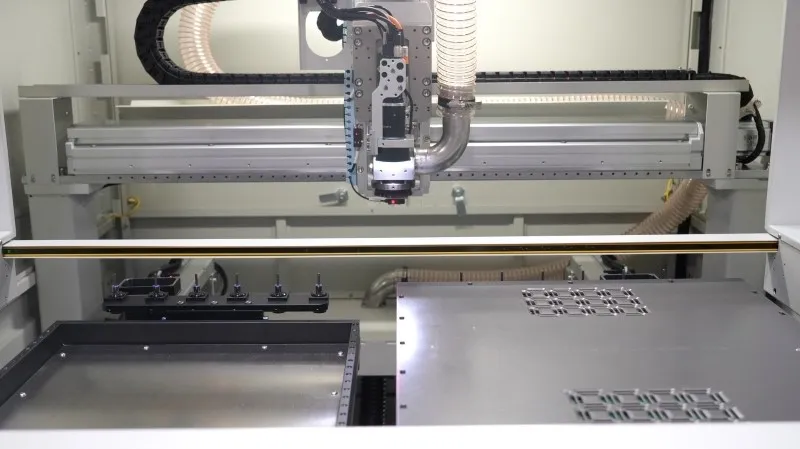
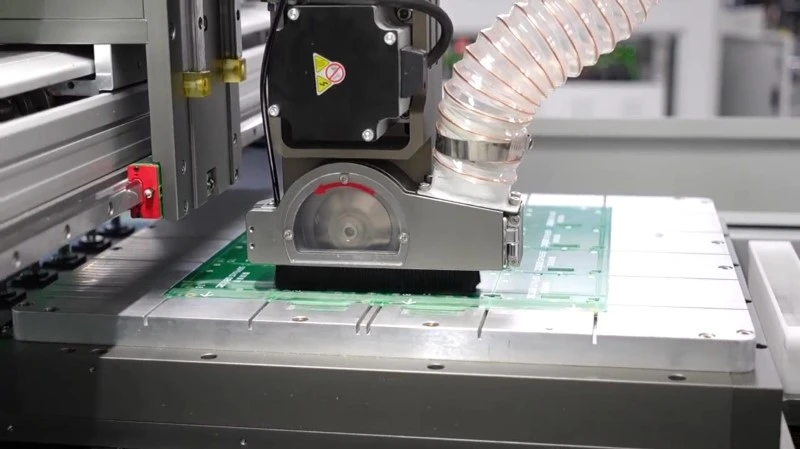
What is the Working Principle of Laser Depaneling?
The working principle of laser depaneling involves using a high-energy laser beam to precisely cut through the connecting tabs or routing channels of a PCB (Printed Circuit Board) panel, separating individual boards without mechanical contact. A laser source, such as a CO2 or UV laser, generates a focused beam that is directed onto the PCB material through an optical system.
When the laser interacts with the material, its energy is absorbed, causing localized heating and vaporization (ablation) along the programmed cutting path. This process is controlled by software that guides the laser head with high precision, enabling the creation of complex shapes and fine details to be cut cleanly. Since laser depaneling is a non-contact method, it eliminates mechanical stress, reduces the risk of damage to sensitive components, and produces minimal debris, making it ideal for high-density and delicate PCB designs.
What Types of Lasers are Used in Laser Depaneling?
CO2 Lasers:
- Best for cutting non-metal materials, such as FR-4 (a common PCB material).
- Fast and cost-effective, but can’t cut metals well.
UV Lasers:
- Great for high-precision cutting, especially for flexible PCBs or materials with copper.
- Very accurate with minimal heat damage, but slower and more expensive.
Green Lasers:
- Used for specific materials like flexible circuits.
- Offers good precision but is less common and more costly.
Fiber Lasers:
- Used for cutting metal-based PCBs.
- Efficient for metals but not suitable for non-metal materials.
Femtosecond Lasers:
- Ultra-high precision with almost no heat damage.
- Ideal for delicate materials, but very expensive and slow.
Picosecond Lasers:
- Similar to femtosecond lasers but slightly less precise.
- Still high-cost and used for advanced applications.
Excimer Lasers:
- Used for very precise cutting of special materials.
- High resolution but expensive and complex to maintain.
What are the Differences Between CO2 Lasers and UV Lasers in Depaneling Applications?

What are the Differences Between Laser Depaneling and Traditional Mechanical Depaneling?
Seprays’ Laser PCB Depaneling Solutions
Лазерная резка печатных плат ZAM310/FPC
SEPRAYS’ZAM310 PCB/FPC Laser cutting machines ensure that no stress is imparted to nearby components, even when the cutting path is very close to them. To further minimize thermal impact, lasers are carefully selected based on thermal requirements, and their processing parameters are precisely matched to optimize performance.
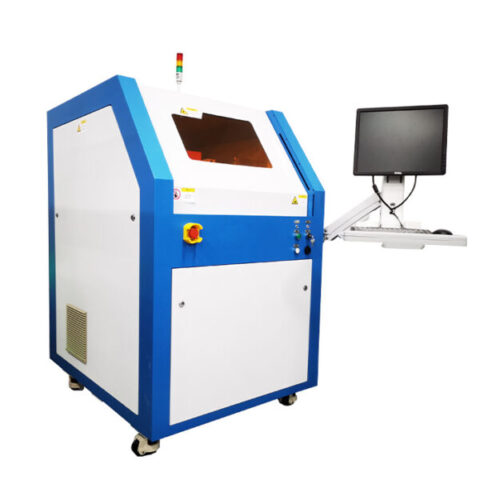

Станок для лазерной резки печатных плат ZAM320/FPC
SEPRAYS’ZAM320 PCB/FPC Laser Cutting Machine has a compact design and can save factory space. A variety of nanosecond, picosecond UV, and green lasers are available to meet various processing needs.

Conclusion
Laser depaneling is a major improvement in PCB manufacturing, offering precise, clean cuts without damaging sensitive components. By understanding how it works and the types of lasers used, manufacturers can choose the best method for their needs. As electronics continue to get smaller and more complex, laser depaneling will become even more important. With its ability to cut delicate designs without stress or debris, laser depaneling is shaping the future of electronics production.
.png)