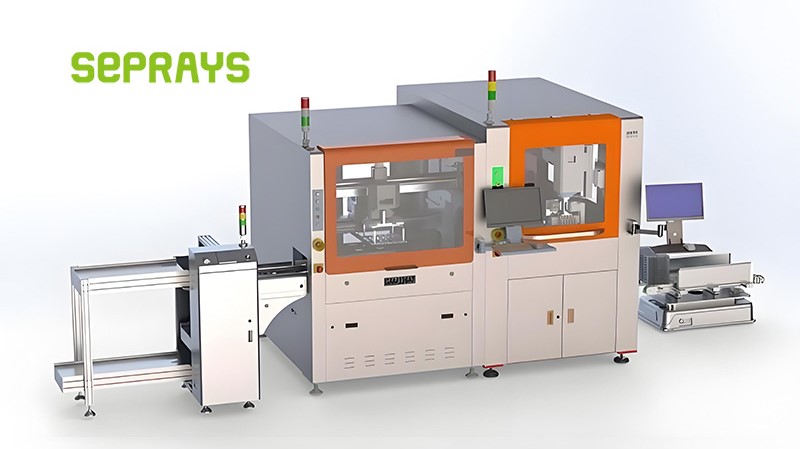
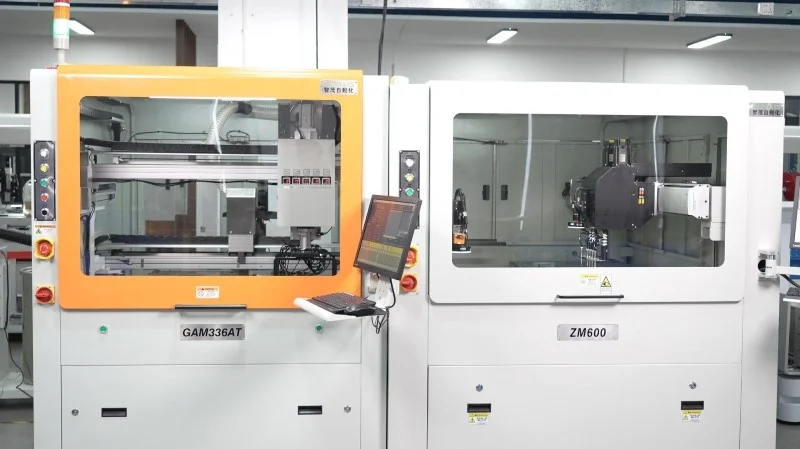
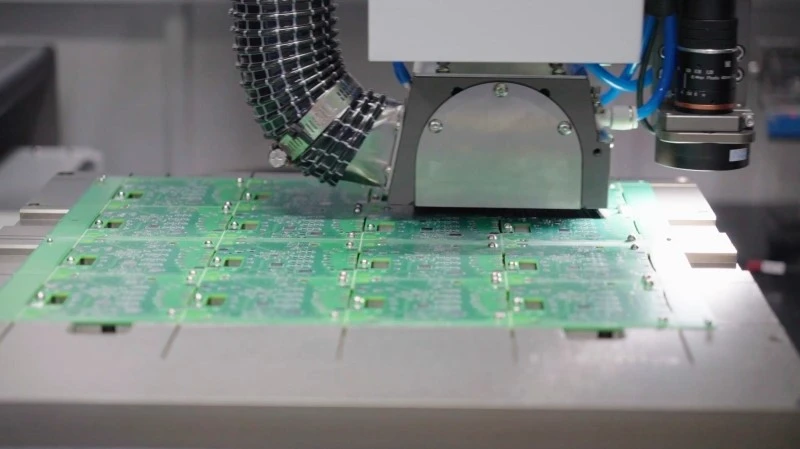
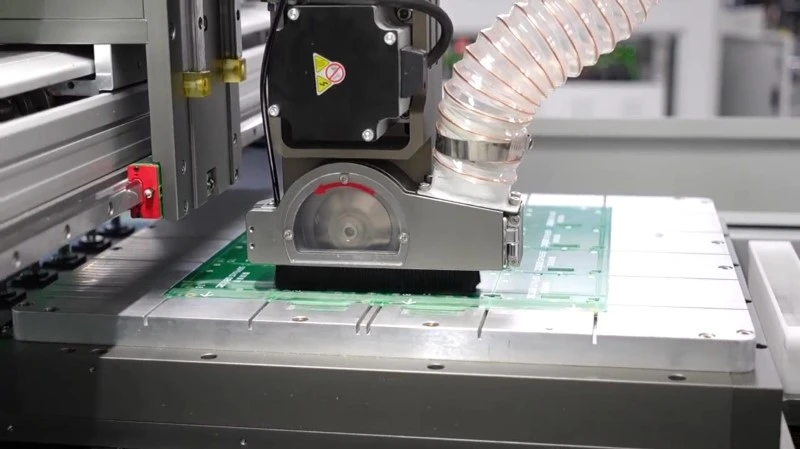
In the precision-driven world of electronics manufacturing, depanelers—the core equipment for PCB (printed circuit board) separation—play a crucial role. They precisely divide large, contiguous circuit boards into individual units, ensuring flawless quality while protecting delicate circuitry. By combining mechanical control, vision positioning, and material mechanics, depanelers achieve millimeter-level accuracy. Whether using a high-speed milling cutter or a laser beam, they deliver smooth, burr-free edges while minimizing internal damage.

From Traditional to Intelligent: The Evolution of Depaneler Technology
Early depanelers relied on manual positioning and fixed cutting paths. This limited both efficiency and accuracy. Today, thanks to Industry 4.0 advancements, modern depanelers are far more intelligent:
- CCD vision systems automatically identify board markers.
- Force feedback control ensures low-stress, stable cutting.
- Adaptive algorithms adjust parameters in real time.
- AI learning even optimizes cutting paths for unusual shapes or dense wiring layouts.
For example, when working on high-density PCBs, the machine can dynamically adjust spindle speed and feed rate to prevent stress cracks in fragile substrates.

Structural Categories: In-Line vs. Offline
Depanelers are typically classified into two main categories:
- In-line depanelers – Integrated directly into SMT (surface mount technology) production lines, they automatically separate boards after placement. Best for high-volume, standardized production.
- Offline depanelers – Independent systems ideal for small-batch or high-mix orders, offering greater flexibility.
Cutting methods include milling, laser, and stamping. Milling is the mainstream choice due to its cost-effectiveness and wide applicability. Laser cutting offers unmatched precision but at higher costs. Stamping excels in specific fixed-shape boards but is limited by tooling requirements.

Why Performance Matters
The performance of a depaneler directly impacts product quality and production efficiency. Key considerations include:
- Cutting accuracy: Typically controlled within ±0.05mm, ensuring pad-to-edge spacing meets design standards.
- 절단 속도: High-end equipment reaches several meters per minute, balancing speed with stability to prevent vibration or delamination.
- Dust control: Glass fibers and copper debris can contaminate boards or damage guide rails. To address this, most modern depanelers use negative-pressure dust removal systems and sealed cutting chambers.
The Depaneling Process: Five Key Steps
- Loading – Robotic arms or conveyors position PCBs onto the worktable.
- Positioning – CCD cameras capture fiducials, while the system auto-corrects alignment.
- Cutting – Milling cutters follow preset paths, with sensors monitoring cutting force in real time.
- Dust Removal – High-pressure airflow extracts debris into precision filters.
- Unloading – Finished boards are inspected and discharged automatically.
This fully automated workflow reduces single-board processing to just a few seconds.
New Challenges for Next-Generation Electronics
As devices become thinner and more integrated, depanelers face growing technical challenges:
- Flexible printed circuits (FPCs): Require advanced tension control to prevent warping.
- 5G substrates (e.g., PTFE): Sensitive to heat, requiring cryogenic milling or water-cooled cutting.
- Environmental compliance: Stricter dust-emission regulations are pushing the adoption of advanced filtration and cleanroom-ready solutions.

The Future of Depaneling
Depanelers are the “Unsung Heroes” of electronics manufacturing, but their role is pivotal. From smartphones to EVs, medical devices to aerospace systems, every precision circuit board depends on accurate separation.
Looking forward, breakthroughs in materials science, control systems, and AI integration will drive depanelers toward even greater precision, flexibility, and intelligence. These innovations will not only improve quality but also accelerate the ongoing transformation of the global electronics industry.
.png)