PCB depaneling is a critical process in electronics manufacturing. It directly affects board quality and component reliability. This article analyzes seven common depaneling methods: manual breaking, die cutting, sliding-type depaneling, guillotine cutting, saw blade separation, milling (router) depaneling, and laser cutting.
1. Manual Depaneling
Manual depaneling includes two types: by hand or with tools such as pliers or fixtures.
Using fixtures improves efficiency compared to cutting with pliers. This method is often referred to as manual breaking.

Advantages:
- No equipment investment needed.
- Only basic tools (pliers, saw, sandpaper).
- Low cost per use.
- Suitable for simple depaneling tasks.
Disadvantages:
- Can leave burrs and uneven edges.
- Only suitable for boards without edge connectors or components.
- Not recommended for V-cut connections due to high mechanical stress.
- May damage components even on bare boards.

Manual depaneling is best for “stamp hole” connected PCBs with low-stress connections. For other connection types, this method is not advised.
2. Die Cutting
Die cutting uses specialized molds for fast, batch depaneling. It’s ideal for V-cut connected PCBs in medium production volumes.
Advantages:
- Very high efficiency.
- Ideal for mid-sized batch production.
Disadvantages:
- Requires expensive custom molds.
- High cutting stress may damage SMD components.

3. Sliding vs. Cutter Wheel Depaneling

Both methods are suitable for V-cut PCBs.
Sliding Type:
- Blade stays fixed; the operator pushes the board through.
- The lower blade drives the motion; the upper blade follows.
- Not widely used today.
Cutter Wheel Type:
- PCB stays still while a rotating blade moves side-to-side.
- Common and cost-effective method.
- Can introduce PCB stress, but good design can reduce this.

Advantages:
- Efficient and simple for straight cuts.
- Cost-effective for general use.
Disadvantages:
- May cause burrs and dust.
- Some mechanical stress during cutting.
4. Guillotine Depaneling
This method is similar to a paper cutter, using a straight blade to cut through V-cut PCBs.
Advantages:
- Easy to operate and safe.
- Low cost.
- Good for standard V-cut panels.
Disadvantages:
- Only suitable for V-cut panels.
- Blades require regular maintenance.
- Manual process limits productivity.

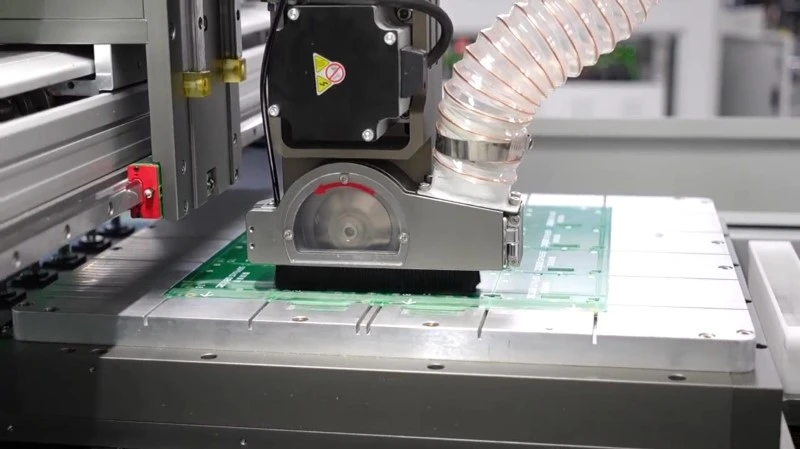
5. Saw Blade Depaneling
Uses high-speed rotating blades (e.g., diamond or carbide) to cut PCBs.
Works for both V-cut and stamp hole panels.

Advantages:
- Faster than manual depaneling.
- Suitable for thicker boards or those with some components.
- Good for small to mid-volume production.
Disadvantages:
- Can produce rough edges.
- Generates a lot of debris.

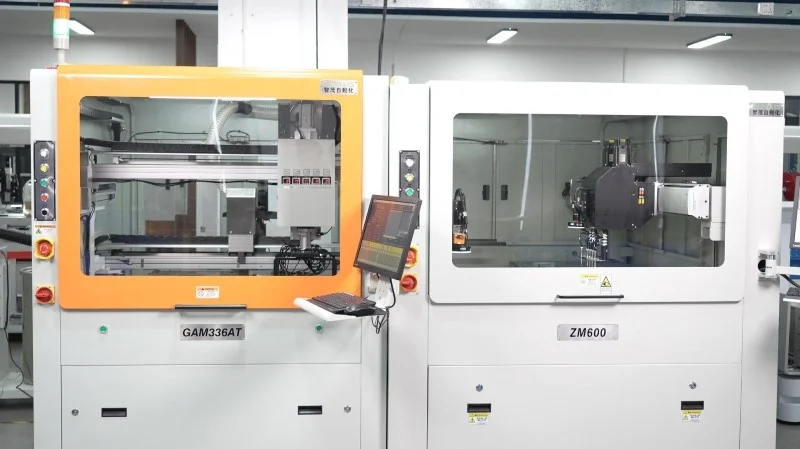
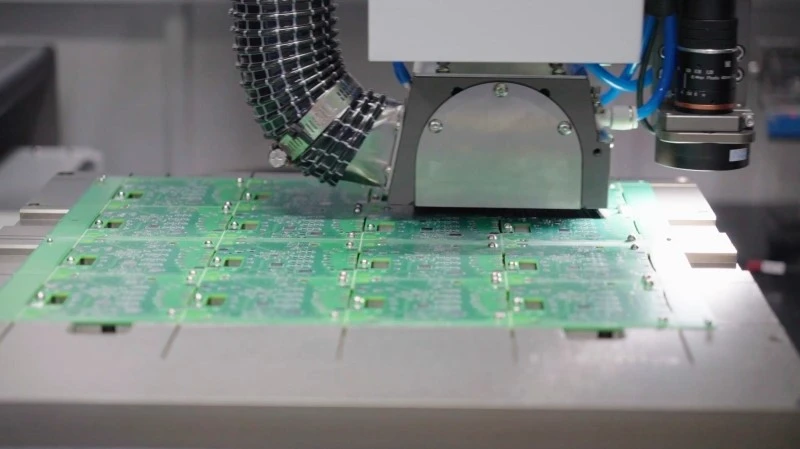
6. Milling (Router) Depaneling
Also known as CNC depaneling or routing. Uses a high-speed spindle and milling bit to cut through connection points. Common in PCB manufacturing.
Advantages:
- Cuts any shape, not just straight lines.
- Minimal mechanical stress on components.
- Smooth, precise cuts with no burrs.
- Low impact on PCB layout design.
Disadvantages:
- Generates dust, requiring dust removal systems.
- Expensive equipment.
- Fixtures must be custom-made for each product.

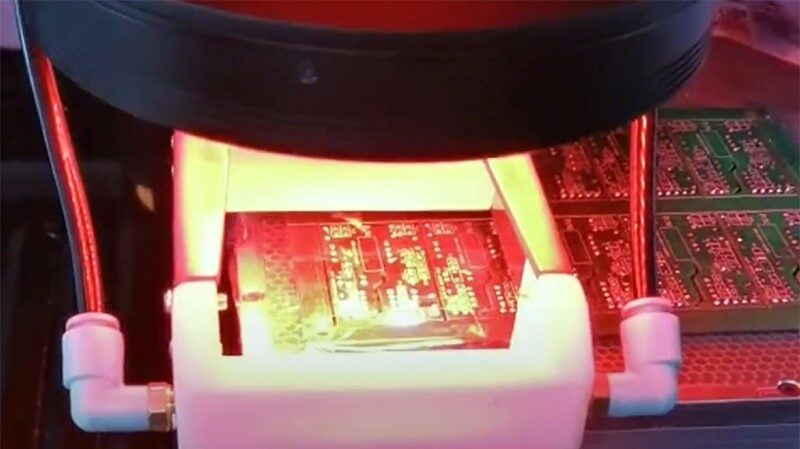
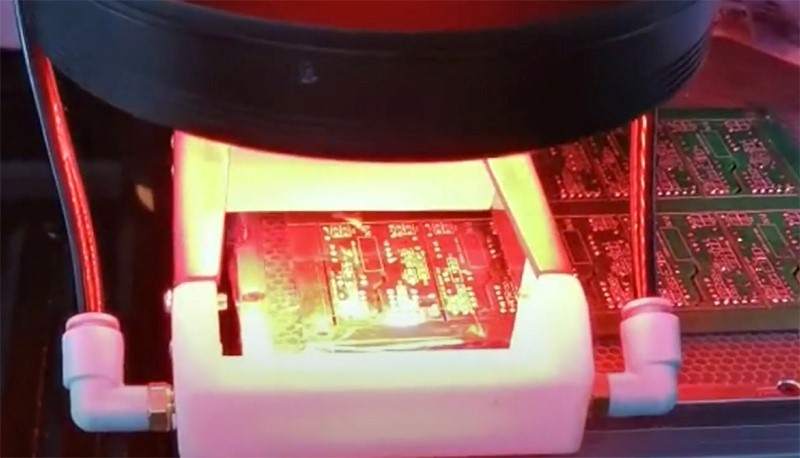
7. Laser Depaneling
Laser cutting uses high-energy beams to precisely separate PCBs. Suitable for complex, high-precision layouts or special materials.
Advantages:
- Ultra-high precision.
- No mechanical stress.
- No blade wear.
Disadvantages:
- High equipment cost.
- Less efficient on thick boards.
- Requires skilled operation.
Conclusión
Choose the right depaneling method based on your product’s precision, volume, and cost needs.
- Manual, saw blade, and die cutting work for low-cost or low-volume jobs.
- Milling and laser cutting are ideal for high-precision, high-density, or sensitive PCBs.
.png)